Boot Linux From Usb Mac For Everything
Clover Boot Disk is the name after you have a USB bootable via Clover. I have not tested on the official MAC. It works for Hackintosh machines. Clover Boot Disk supports both Legacy BIOS and UEFI modes, because Clover supports both modes. This article does not instruct you to use Clover Bootloader, as well as install macOS.
If you've ever wiped your computer without having a proper backup of your operating system, or just wanted to, chances are you've had to rely on Linux to help you out, specifically the distro. Ubuntu doesn't get a lot of love compared to powerhouses like and, but those who do use it are often fans for life. It is currently the most popular Linux distribution and has a dedicated community that's actively working to make it smoother, faster, and more secure. Since it's based off of Linux, it has the ability to boot on pretty much anything, from a USB drive to. While it's pretty impressive that a can handle an entire operating system, it won't help you get your computer up and running. In this guide, I'm going to show you how to create a USB drive that contains all of the necessary files to boot your Windows PC or Mac into Ubuntu.

To create this bootable USB drive, also known as a live USB, you will need access to a USB drive with at least 2 GB of storage and a functioning computer, but it does not matter if it is a Mac or Windows. In addition, you will also need a copy of the latest version of Ubuntu, which can be downloaded from. Installation for Windows Users If you have access to a Windows machine, the process of creating a live USB is extremely easy.
All you have to do is download the from. When it's done, you can boot directly into Ubuntu by selecting the USB drive from your Boot Devices. The way to access the the Boot Devices menu varies between manufacturers, but it can usually be accessed by pressing one of the F keys right after powering on your computer.
After a customer accepts your estimate, you can easily turn it into an invoice for billing. (If you want to partially invoice your customer, use progress invoicing instead.) Here's how to convert an estimate/quote into an invoice: From the left menu, select Sales, then choose All Sales. Find and open the estimate/quote. Select Create invoice. Convert estimates to invoices Once a new estimate is accepted, QuickBooks will convert the estimate to invoices for you. Some businesses may choose to take a deposit at the beginning of the job and invoice for the remaining amount at the end. 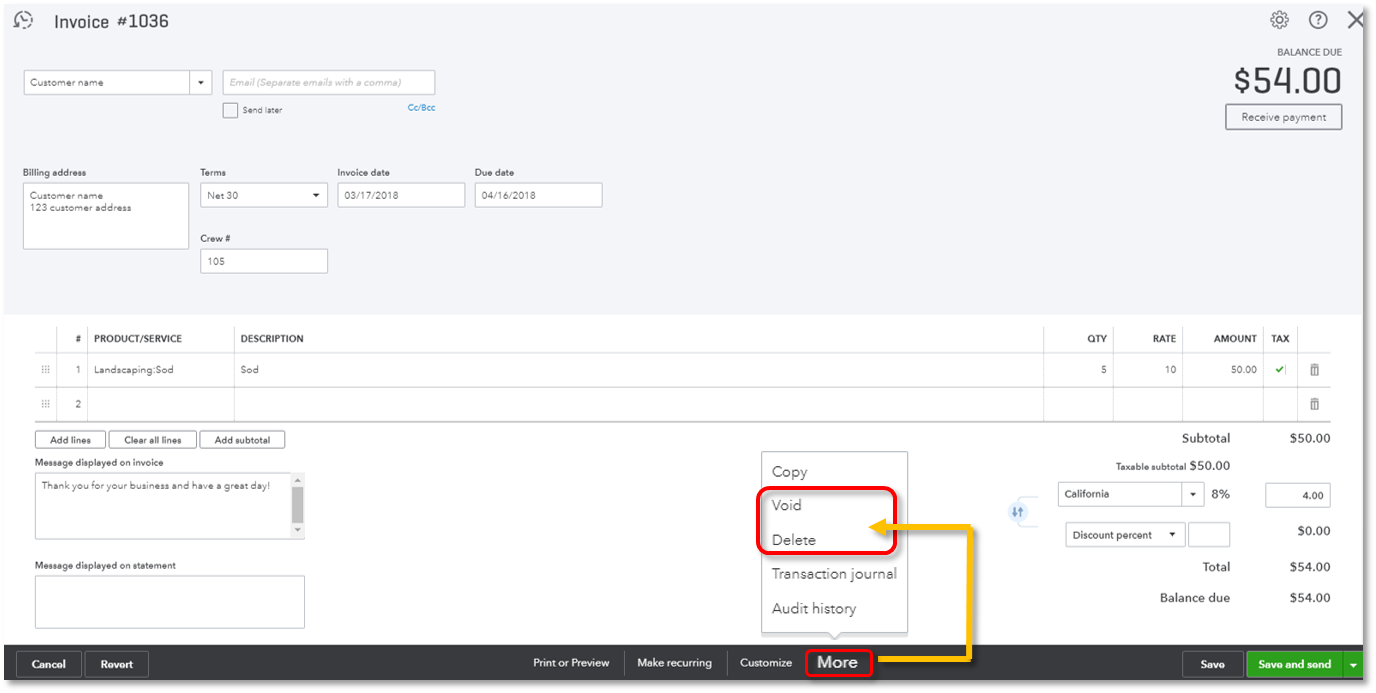 QuickBooks automatically applies 100 percent of labor costs when you convert an estimate to an invoice, but you may need to set the percentages for materials costs manually.
QuickBooks automatically applies 100 percent of labor costs when you convert an estimate to an invoice, but you may need to set the percentages for materials costs manually.
Once you select your live USB disk and your system boots up, choose the option to 'Try Ubuntu Without Installing' and wait for the operating system to start. Installation for Mac Users Unfortunately, Mac OS X does not have a tool like Universal USB Installer to create a live USB, but as a Mac user, you should be used to that feeling by now and know that it isn't a big deal. Instead of using a traditional app, we will use. You should now see a list of all the drives attached to your Mac. Look for your USB drive and take note of the number after /dev/disk. If you are unsure which disk is associated with USB drive, you can unplug your drive, enter the previous command, plug your USB drive back in, enter the command one more time, and then compare the two outputs to find your USB drive's node Once you have that node number, you can use it to flash the the.img file with the following commands. Colecovision adam emulator for pc.

Be sure to replace the # symbols with your node number and run each command separately. When it asks for you admin password, make sure to enter it and continue on. Also, make sure to replace 'Desktop' if your.img file is somewhere else. Diskutil unmountDisk /dev/disk# sudo dd if=Desktop/Ubuntu.img of=/dev/rdisk# bs=1m diskutil eject /dev/disk#.